This text is a draft part from my banking manuscript. It matches right into a chapter on financial institution threat administration. This text is an introduction to primary chapter procedures, which must be understood earlier than worrying about how banks handle the danger of their prospects defaulting. This model of the part consists of some textual content about financial institution decision procedures that was beforehand printed (however modified right here).
Earlier than discussing credit score threat administration, we have to give some background on credit score threat itself. Usually, credit score losses will outcome from restructurings or chapter procedures. This part offers a high-level dialogue of the logic behind chapter procedures. It additionally features a dialogue of how American financial institution failures are resolved. (The American banking system produces a excessive quantity of financial institution failures, and so it has probably the most developed system for managing the method.)
Chapter Safety
If some entity owes you cash and refuses to pay, the usual recourse is to resort to authorized motion. Non-payment could also be the results of a disagreement whether or not contractual phrases had been met, and corporations can function usually despite the fact that it’s in courtroom. Nevertheless, if a agency is on the point of insolvency, it might not be capable of meet its contractual funds. In idea, each entity owed cash may rush to courtroom after which try and seize property to repay their money owed. Such a rush of litigation and judgements would destroy the viability of the agency and would end in unfair outcomes – the primary events to get to courtroom would receives a commission off in full, whereas the later events would possible get nothing.
The inadequacy of counting on adjudicating contracts separately resulted in international locations enacting statutes regulating bankruptcies. People with comparatively small money owed function underneath simplified guidelines, whereas giant instances find yourself in courtroom. For enterprise bankruptcies, the target is to seek out an final result that greatest serves all events to the chapter: workers (and administration), prospects, maintaining the agency working, in addition to the collectors. Completely different international locations weigh the differing claims in a different way, and the authorized procedures differ. Chapter judges have appreciable energy to find out the outcomes, which forces the events to be versatile of their negotiations since they can not assure that the choose will rule of their favour based mostly on the legal guidelines.
Companies that concern insolvency go to a chapter courtroom looking for chapter safety. This places the agency in a authorized standing (of which there are sometimes just a few variants) that defend the agency from any makes an attempt by collectors to grab property. The chapter process then includes figuring out all claimants, after which negotiating an answer.
There are two broad methods of ending a enterprise chapter. Both the agency restructures its money owed (contracts are renegotiated for ones which are less expensive for the debtor) or the agency is liquidated. In a liquidation, all property are auctioned off, and the proceeds are used to pay collectors so as of precedence. For industrial corporations, the restoration on liquidation is usually decrease than a restructuring. For corporations that borrowed in opposition to monetary devices or actual property, recoveries may be greater.
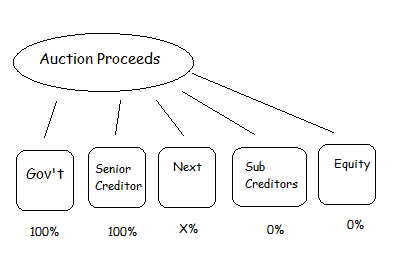
Liquidation Precedence
If a bankrupt agency is liquidated, all its property are bought, typically in auctions or related strategies. This may take appreciable time, however for our functions right here, assume that it occurs unexpectedly. For now, assume that no property have been used as collateral for loans.
The diagram above exhibits what occurs subsequent. All collectors are organised into “courses” based mostly on chapter regulation. Every credit score declare’s greenback quantity acts as “share” inside the class, and the category has a complete quantity as a consequence of it which the sum of all of the claims in that class.
The fee proceeds are then paid out to these courses, so as. Authorities taxes receives a commission first (in fact). After that, funds are made to courses so as, till the funds raised in public sale run out. Within the diagram, the “Senior Creditor” will get paid out in full (100%). The “Subsequent” class makes use of up the public sale proceeds, however with a shortfall. Each declare within the class is paid out the identical proportion (“X%”) of the declare quantity. All of the courses beneath that class (theoretically) get nothing. (It’s attainable that subordinated teams will find yourself with one thing after negotiations, since they’ve an incentive to tug out the pricey authorized course of.)
Banks usually be sure that their loans are senior to all of the collectors, together with unsecured bonds. The unique house owners of the agency (“Fairness”) is all the time on the backside of the precedence record and bought 0% on this instance.
The potential for a liquidation determines the bargaining energy of events in chapter negotiations. For the reason that general restoration underneath a restructuring is usually greater than underneath a liquidation (and the chapter course of is pricey), junior collectors nonetheless have a capability to extract some concessions with a view to permit a restructuring to happen.
American Financial institution Decision Procedures
Financial institution chapter is extra sophisticated, and so tends to be handled in a different way than the failure of commercial corporations. Banking laws differ by nation, and the identical is true for the way failing banks are resolved. This article is going to simply use the American system for instance, on the idea that American financial institution failures are extra widespread than in different developed international locations. The price of having a fragmented banking system is that small banks are extra fragile and can’t make investments closely in threat administration.
The important thing distinction between the generic agency chapter course of and financial institution decision in the US is that the Federal Deposit Insurance coverage Company (FDIC) administers the chapter underneath the Federal Deposit Insurance coverage Act. Completely different courses of collectors make claims, however don’t negotiate a decision — it’s imposed by the FDIC. (The technical element on this part depends on an article by Robert R. Bliss and George G. Kaufman listed within the references part.)
The Act creates two courses of super-senior collectors: insured deposits, and uninsured deposits. On the time of writing, the insurance coverage restrict on deposit accounts was $250,000, which meant {that a} depositor with a $1 million deposit would have two claims: a $250,000 insured deposit, and a $750,000 uninsured deposit.
The same old decision process is that FDIC brokers swoop in on Friday after the shut of enterprise, shutter the financial institution, and a few new financial institution (probably operated by the FDIC, or one other financial institution assuming the failed financial institution) is open for enterprise on Monday. (The Silicon Valley Financial institution failure on March 10, 2023 was uncommon in that some geniuses organised a financial institution run over social media, forcing the FDIC to close down the financial institution throughout enterprise hours.) The target is to minimise the disruption for depositors.
The FDIC permits insured depositors to withdraw money from the brand new financial institution. This creates a drain on FDIC funds, which is matched by the FDIC assuming (subrogating) the unique declare. (Subrogating is a cool phrase and must be used extra.) Because of this the outflow doesn’t have an effect on the waterfall of claims on the financial institution property, simply strikes the declare from the unique depositor to the FDIC.
For uninsured deposits, they usually get a declare certificates that could be a negotiable instrument. That’s, they’ll promote the declare at a reduction to boost money. Within the Silicon Valley Financial institution chapter, the FDIC waived this situation and supplied a full assure on uninsured deposits (which I’ll talk about beneath), so the 2 courses of deposits ended up merged.
For the reason that depositors (and subrogated FDIC) have precedence, they receives a commission earlier than all different courses of collectors. Because of this the FDIC solely takes a monetary loss on a financial institution failure if the losses from the failed financial institution blow by way of each different layer of the financial institution’s capital construction — fairness, most popular fairness, and all the assorted seniorities of bonds. (The FDIC will even incur administrative prices in the course of the exercise.) Since regulators are supposed to make sure that losses are lower than the fairness of the financial institution — by no means thoughts the opposite layers of capital – that requires a considerably drastic regulatory failure for such losses to point out up. Deposits are speculated to be secure, and all the opposite layers of the capital construction are sacrificed to make them so.
The Silicon Valley Financial institution
The Silicon Valley Financial institution (SVB hereafter) was an uncommon establishment and acts a counterexample to what I argue is commonplace threat administration practices at giant banks.
Silicon Valley Financial institution began as a small financial institution, however it grew alongside facet the enterprise capital trade in Silicon Valley. Its mum or dad firm (Silicon Valley Financial institution Monetary Group) amassed $212 billion in property forward of the group’s failure. Regardless of its measurement, it didn’t face the identical stringent regulation that international systemically essential banks (G-SIBs) face. (The Federal Reserve printed a abstract of its evolution in addition to the causes of the failure that’s cited beneath.)
The underlying issues with SVB the place focus and length threat. The financial institution relied on giant deposits coming from a single native trade, and people trade members had been in fixed contact with one another. This created focus threat for its funding. The financial institution wanted a particularly giant liquidity portfolio to handle that liquidity threat, however SVB administration successfully rolled the cube on rates of interest and had a big hold-to-maturity bond portfolio. The market worth of that portfolio was shattered by the bond bear market, and the spectre of insolvency hung over the financial institution. Though it limped alongside for awhile, it was lastly put out of enterprise by the run of enormous depositors. (The article by Cipriani, Eisenbach, and Kovner within the references examined funds system knowledge and located that the outflows had been concentrated amongst giant depositors, retail depositor behaviour didn’t seem uncommon.)
The FDIC was criticised for bailing out the uninsured depositors, however this was justifiable on systemic threat grounds. There was widespread fearmongering about different banks failing as a consequence of losses on their bond portfolios, and the bailout was presumably supposed to forestall this by demonstrating to depositors that they’d be made entire.
Concluding Remarks
With the background data on chapter procedures out of the way in which, we will subsequent have a look at how banks handle their credit score threat.
References and Additional Studying
E-mail subscription: Go to https://bondeconomics.substack.com/
(c) Brian Romanchuk 2024